What Can GIS Do for You?
The ability of GISs to search databases and perform geographic queries has saved many companies literally millions of dollars. GISs have helped reduce costs by
- Streamlining customer service.
- Reducing land acquisition costs through better analysis.
- Reducing fleet maintenance costs through better logistics.
- Analyzing data quickly, as in this example:
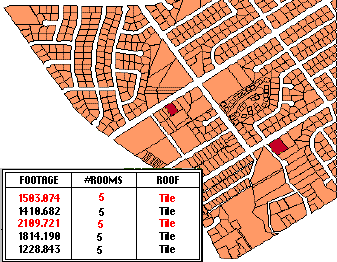
A realtor could use a GIS to find all houses within a certain area that have tiled roofs and five bedrooms, then list their characteristics.
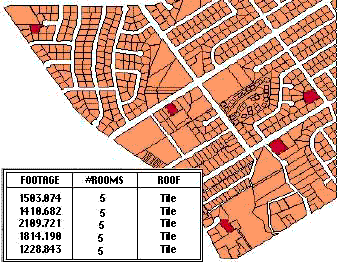
The query could be further refined by adding criteria - the house must cost less than $100 per square foot. You could also list houses within a certain distance of a school.
Improve Organizational Integration
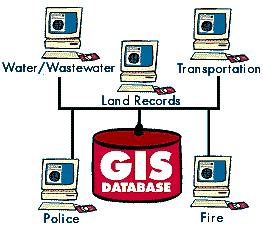
Many organizations that have implemented a GIS have found that
one of its main benefits is improved management of their own organization and resources. Because GISs have the ability to link data sets together by geography, they facilitate interdepartmental information sharing and communication. By creating a shared database, one department can benefit from the work of another - data can be collected once and used many times.
|
As communication increases among individuals and departments, redundancy is reduced, productivity is enhanced, and overall organizational efficiency is improved. Thus, in a utility company the customer and infrastructure databases can be integrated so that when there is planned maintenance, affected customers can be sent a computer-generated letter. |
 |
|
Make Better Decisions
The old adage "better information leads to better decisions" is
as true for GIS as it is for other information systems. A GIS,
however, is not an automated decision making system but a tool
to query, analyze, and map data in support of the decision making
process. GIS technology has been used to assist in tasks such
as presenting information at planning inquiries, helping resolve
territorial disputes, and siting pylons in such a way as to minimize
visual intrusion.
GIS can be used to help reach a decision about the location of a new housing development that has minimal environmental impact, is located in a low-risk area, and is close to a population center. The information can be presented succinctly and clearly in the form of a map and accompanying report, allowing decision makers to focus on the real issues rather than trying to understand the data. Because GIS products can be produced quickly, multiple scenarios can be evaluated efficiently and effectively.
Making Maps
Maps have a special place in GIS. The process of making maps with
GIS is much more flexible than are traditional manual or automated
cartography approaches. It begins with database creation. Existing
paper maps can be digitized and computer-compatible information
can be translated into the GIS. The GIS-based cartographic database
can be both continuous and scale free. Map products can then be
created centered on any location, at any scale, and showing selected
information symbolized effectively to highlight specific characteristics.
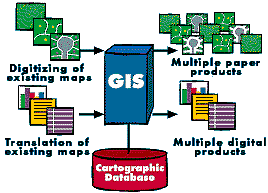
The characteristics of atlases and map series can be encoded in computer programs and compared with the database at final production time. Digital products for use in other GISs can also be derived by simply copying data from the database. In a large organization, topographic databases can be used as reference frameworks by other departments.
