Components of a GIS
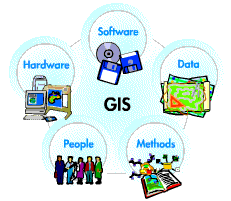 A
working GIS integrates five key components: hardware,
software, data, people, and methods.
A
working GIS integrates five key components: hardware,
software, data, people, and methods.
Hardware
Hardware is the computer on which a GIS operates.
Today, GIS software runs on a wide range of hardware
types, from centralized computer servers to desktop
computers used in stand-alone or networked
configurations.
Software
GIS software provides the functions and tools needed
to store, analyze, and display geographic information.
Key software components are
- Tools for the input and manipulation of geographic information
- A database management system (DBMS)
- Tools that support geographic query, analysis, and visualization
- A graphical user interface (GUI) for easy access to tools
Data
Possibly the most important component of a GIS is the
data. Geographic data and related tabular data can be
collected in-house or purchased from a commercial data
provider. A GIS will integrate spatial data with other
data resources and can even use a DBMS, used by most
organizations to organize and maintain their data, to
manage spatial data.
People
GIS technology is of limited value without the people
who manage the system and develop plans for applying
it to real-world problems. GIS users range from
technical specialists who design and maintain the
system to those who use it to help them perform their
everyday work.
Methods
A successful GIS operates according to a well-designed
plan and business rules, which are the models and
operating practices unique to each organization.
